- 자바 프로그래밍(com.eomcs.io)
- File 클래스 사용법(ex01)
File 클래스 사용법(ex01)
폴더 정보 조회 - java.io.File 클래스
Exam0110.java
package com.eomcs.io.ex01;
import java.io.File;
public class Exam0110 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
File currentDir = new File("./src/main/java");
System.out.printf("폴더명: %s\n", currentDir.getName());
System.out.printf("경로: %s\n", currentDir.getPath());
System.out.printf("절대경로: %s\n", currentDir.getAbsolutePath());
System.out.printf("계산된 절대경로: %s\n", currentDir.getCanonicalPath());
System.out.printf("총크기: %d\n", currentDir.getTotalSpace());
System.out.printf("남은크기: %d\n", currentDir.getFreeSpace());
System.out.printf("가용크기: %d\n", currentDir.getUsableSpace());
System.out.printf("디렉토리여부: %b\n", currentDir.isDirectory());
System.out.printf("파일여부: %b\n", currentDir.isFile());
System.out.printf("감춤폴더: %b\n", currentDir.isHidden());
System.out.printf("존재여부: %b\n", currentDir.exists());
System.out.printf("실행가능여부: %b\n", currentDir.canExecute());
}
}
ㄴ File 클래스
=> 디렉토리나 파일을 다룰 때 사용하는 클래스
=> 디렉토리나 파일을 생성, 삭제, 변경할 수 있음
ㄴ 현재 디렉토리를 조회
=> '.' 으로 표현
=> JVM을 실행하는 위치가 현재 폴더임
=> 이클립스 : 프로젝트 디렉토리를 가리킴
=> 콘솔 : 현재 명령어를 실행하는 위치를 가리킴
ㄴ 계산된 절대경로 => . 이나 .. 같은 것들을 제외시킨 경로
폴더 정보 조회 - java.io.File 클래스
Exam0120.java
package com.eomcs.io.ex01;
import java.io.File;
public class Exam0120 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
File currentDir = new File("./src/main/java/../../test/java");
System.out.printf("폴더명: %s\n", currentDir.getName());
System.out.printf("경로: %s\n", currentDir.getPath());
System.out.printf("절대경로: %s\n", currentDir.getAbsolutePath());
System.out.printf("계산된 절대경로: %s\n", currentDir.getCanonicalPath());
System.out.printf("총크기: %d\n", currentDir.getTotalSpace());
System.out.printf("남은크기: %d\n", currentDir.getFreeSpace());
System.out.printf("가용크기: %d\n", currentDir.getUsableSpace());
System.out.printf("디렉토리여부: %b\n", currentDir.isDirectory());
System.out.printf("파일여부: %b\n", currentDir.isFile());
System.out.printf("감춤폴더: %b\n", currentDir.isHidden());
System.out.printf("존재여부: %b\n", currentDir.exists());
System.out.printf("실행가능여부: %b\n", currentDir.canExecute());
}
}
ㄴ 상위 폴더 정보 조회
=> ".." 으로 경로를 표시
Exam0130.java
package com.eomcs.io.ex01;
import java.io.File;
public class Exam0130 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
File currentDir = new File("./haha");
System.out.printf("폴더명: %s\n", currentDir.getName());
System.out.printf("경로: %s\n", currentDir.getPath());
System.out.printf("절대경로: %s\n", currentDir.getAbsolutePath());
System.out.printf("계산된 절대경로: %s\n", currentDir.getCanonicalPath());
// 존재하지 않는 폴더인 경우 크기는 0이다.
System.out.printf("총크기: %d\n", currentDir.getTotalSpace());
System.out.printf("남은크기: %d\n", currentDir.getFreeSpace());
System.out.printf("가용크기: %d\n", currentDir.getUsableSpace());
// 존재하지 않는 폴더인 경우 정보를 알아낼 수 없다. 모두 false
System.out.printf("디렉토리여부: %b\n", currentDir.isDirectory());
System.out.printf("파일여부: %b\n", currentDir.isFile());
System.out.printf("감춤폴더: %b\n", currentDir.isHidden());
System.out.printf("존재여부: %b\n", currentDir.exists());
System.out.printf("실행가능여부: %b\n", currentDir.canExecute());
}
}
ㄴ 존재하지 않는 폴더는 크기 0
ㄴ 존재하지 않는 폴더 조회 시 false 출력됨
파일 정보 조회 - java.io.File 클래스
Exam0210.java
package com.eomcs.io.ex01;
import java.io.File;
public class Exam0210 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 현재 파일 정보 조회
File file1 = new File("./src/main/java/Hello2.java");
System.out.printf("파일명: %s\n", file1.getName());
System.out.printf("파일크기: %d\n", file1.length());
System.out.printf("경로: %s\n", file1.getPath());
System.out.printf("절대경로: %s\n", file1.getAbsolutePath());
System.out.printf("계산된 절대경로: %s\n", file1.getCanonicalPath());
// 존재하지 않는 폴더인 경우 크기를 알아낼 수 없다.
System.out.printf("총크기: %d\n", file1.getTotalSpace());
System.out.printf("남은크기: %d\n", file1.getFreeSpace());
System.out.printf("가용크기: %d\n", file1.getUsableSpace());
// 존재하지 않는 폴더인 경우 정보를 알아낼 수 없다. 모두 false
System.out.printf("디렉토리여부: %b\n", file1.isDirectory());
System.out.printf("파일여부: %b\n", file1.isFile());
System.out.printf("감춤여부: %b\n", file1.isHidden());
System.out.printf("존재여부: %b\n", file1.exists());
System.out.printf("실행가능여부: %b\n", file1.canExecute());
}
}

ㄴ 존재하지 않는 파일 조회 시 false 출력됨
Exam0220.java
package com.eomcs.io.ex01;
import java.io.File;
public class Exam0220 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 존재하지 않는 파일 정보 조회
File file1 = new File("./src/main/java/Hello100.java");
System.out.printf("파일명: %s\n", file1.getName());
System.out.printf("파일크기: %d\n", file1.length());
System.out.printf("경로: %s\n", file1.getPath());
System.out.printf("절대경로: %s\n", file1.getAbsolutePath());
System.out.printf("계산된 절대경로: %s\n", file1.getCanonicalPath());
// 존재하지 않는 폴더인 경우 크기를 알아낼 수 없다.
System.out.printf("총크기: %d\n", file1.getTotalSpace());
System.out.printf("남은크기: %d\n", file1.getFreeSpace());
System.out.printf("가용크기: %d\n", file1.getUsableSpace());
// 존재하지 않는 폴더인 경우 정보를 알아낼 수 없다. 모두 false
System.out.printf("디렉토리여부: %b\n", file1.isDirectory());
System.out.printf("파일여부: %b\n", file1.isFile());
System.out.printf("감춤여부: %b\n", file1.isHidden());
System.out.printf("존재여부: %b\n", file1.exists());
System.out.printf("실행가능여부: %b\n", file1.canExecute());
}
}
ㄴ 존재하지 않는 파일이나 폴더는 크기를 알아낼 수 없음
ㄴ 존재하지 않는 파일 조회 시 false 출력됨
디렉토리 생성
Exam0310.java
package com.eomcs.io.ex01;
import java.io.File;
public class Exam0310 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 1) 생성할 디렉토리 경로 설정
// - 폴더 경로를 지정하지 않으면 현재 폴더를 의미한다.
//
File dir = new File("temp");
if (dir.mkdir()) { // 디렉토리 생성
System.out.println("temp 디렉토리를 생성하였습니다.");
} else {
System.out.println("temp 디렉토리를 생성할 수 없습니다.");
}
}
}

=> 생성된 후에 다시 실행 하면 아래와 같이 출력됨

Exam0320.java
package com.eomcs.io.ex01;
import java.io.File;
public class Exam0320 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
File dir = new File("temp/a");
// 하위 디렉토리 생성하기
if (dir.mkdir()) {
System.out.println("temp/a 디렉토리를 생성하였습니다.");
} else {
System.out.println("temp/a 디렉토리를 생성할 수 없습니다.");
}
}
}

=> 생성된 후에 다시 실행 하면 아래와 같이 출력됨

Exam0321.java
package com.eomcs.io.ex01;
import java.io.File;
public class Exam0321 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
File dir = new File("temp2/a");
if (dir.mkdir()) {
System.out.println("temp2/a 디렉토리를 생성하였습니다.");
} else {
System.out.println("temp2/a 디렉토리를 생성할 수 없습니다.");
}
}
}

ㄴ 존재하지 않는 폴더 아래에 새 폴더를 만들 때
=> 존재하지 않는 폴더가 자동 생성되지 않음
=> 따라서 그 하위 폴더를 생성할 수 없음
Exam0322.java
package com.eomcs.io.ex01;
import java.io.File;
public class Exam0322 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
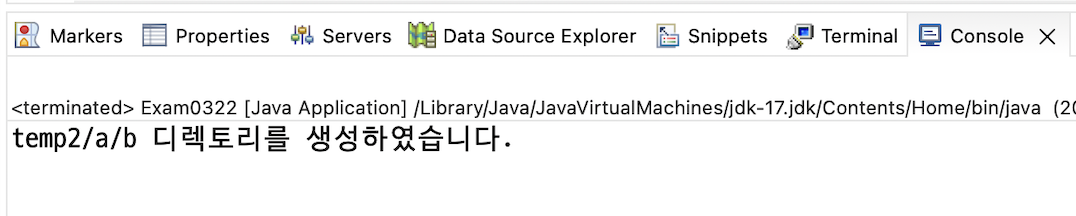
File dir = new File("temp2/a/b");
// 디렉토리를 생성할 때 존재하지 않는 중간 디렉토리도 만들고 싶다면,
// mkdirs()를 호출하라.
//
// mkdirs()
// - 지정된 경로에 디렉토리가 존재하지 않으면 그 디렉토리도 만든다.
//
if (dir.mkdirs()) {
System.out.println("temp2/a/b 디렉토리를 생성하였습니다.");
} else {
System.out.println("temp2/a/b 디렉토리를 생성할 수 없습니다.");
}
}
}
ㄴ 디렉토리를 생성할 때 존재하지 않는 중간 디렉토리도 만들고 싶다면 mkdirs() 호출하면됨
디렉토리 삭제
Exam0330.java
package com.eomcs.io.ex01;
import java.io.File;
public class Exam0330 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
File dir = new File("temp");
if (dir.delete()) {
System.out.println("temp 디렉토리를 삭제하였습니다.");
} else {
System.out.println("temp 디렉토리를 삭제할 수 없습니다.");
}
}
}
ㄴ 디렉토리 안에 파일이나 다른 하위 디렉토리가 있다면 삭제할 수 없음
ㄴ 존재하지 않는 디렉토리도 삭제할 수 없음
파일 생성
Exam0410.java
package com.eomcs.io.ex01;
import java.io.File;
public class Exam0410 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 생성할 파일의 경로 설정
File file = new File("temp2/a/test.txt");
if (file.createNewFile()) { // 파일 생성
System.out.println("test.txt 파일을 생성하였습니다.");
} else {
System.out.println("test.txt 파일을 생성할 수 없습니다.");
}
}
}
ㄴ 이미 파일이 있다면 다시 생성할 수 없음
ㄴ 해당 경로에 디렉토리가 없다면 파일을 생성할 수 없음 => 예외 발생!
Exam0411.java
package com.eomcs.io.ex01;
import java.io.File;
public class Exam0411 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
File file = new File("temp2/b/test.txt");
if (file.createNewFile()) { // 파일 생성
System.out.println("test.txt 파일을 생성하였습니다.");
} else {
// 이미 파일이 있다면 다시 생성할 수 없다.
System.out.println("test.txt 파일을 생성할 수 없습니다.");
}
}
}
ㄴ 존재하지 않는 폴더에 파일을 생성할 때 해당 경로에 디렉토리가 없다면 파일을 생성할 수 없음
=> 예외 발생!
Examp0420.java
package com.eomcs.io.ex01;
import java.io.File;
public class Exam0420 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 삭제할 파일의 경로 설정
File file = new File("temp2/a/test.txt");
if (file.delete()) { // 파일 삭제
System.out.println("test.txt 파일을 삭제하였습니다.");
} else {
System.out.println("test.txt 파일을 삭제할 수 없습니다.");
}
}
}

ㄴ 존재하지 않는 파일은 삭제할 수 없음
=> 경로가 존재하지 않으면 당연히 그 경로에 파일이 없으니까 삭제할 수 없음
특정 폴더를 생성하여 그 폴더에 파일을 만들기
Exam0430.java
package com.eomcs.io.ex01;
import java.io.File;
public class Exam0430 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 생성할 파일의 경로 설정
File file = new File("temp/b/test.txt");
if (file.createNewFile()) { // 파일 생성
System.out.println("test.txt 파일을 생성하였습니다.");
} else {
System.out.println("test.txt 파일을 생성할 수 없습니다.");
}
}
}
ㄴ 디렉토리가 존재하지 않으면 파일을 생성할 수 없다.
=> 예외 발생!
Exam0431.java
package com.eomcs.io.ex01;
import java.io.File;
public class Exam0431 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 생성할 파일의 경로 설정
File file = new File("temp/b/test.txt");
// 파일을 생성하기 전에 존재하지 않는 폴더를 생성하고 싶다면,
// String path = file.getParent(); // => temp/b
// File dir = new File(path);
File dir = file.getParentFile(); // 위의 코드와 같다.
System.out.println(dir.getCanonicalPath());
// 먼저 디렉토리를 생성한다.
if (dir.mkdirs()) {
System.out.println("디렉토리를 생성하였습니다.");
} else {
System.out.println("디렉토리를 생성할 수 없습니다.");
}
// 그런 후 파일을 생성한다.
if (file.createNewFile()) { // 파일 생성
System.out.println("파일을 생성하였습니다.");
} else {
System.out.println("파일을 생성할 수 없습니다.");
}
}
}
ㄴ 존재하지 않는 디렉터리안에 파일을 생성하고 싶으면 mkdirs() 를 먼저 하고 그 후에 createNewFile()을 실행하도록 함
디렉토리에 들어 있는 파일이나 하위 디렉토리 정보 알아내기
Exam0510.java
package com.eomcs.io.ex01;
import java.io.File;
public class Exam0510 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 현재 폴더의 정보를 알아낸다.
File dir = new File(".");
// 현재 폴더에 있는 파일이나 하위 디렉토리 이름을 알아내기
String[] names = dir.list();
for (String name : names) {
System.out.println(name);
}
}
}
ㄴ 현재 폴더의 정보만 알아내려면 File dir = new File("."); 을 이용
ㄴ 현재 폴더에 있는 파일이나 하위 디렉터리 이름을 알아내고 싶으면 String[] names = dir.list(); 를 이용
Exam0520.java
package com.eomcs.io.ex01;
import java.io.File;
import java.sql.Date;
public class Exam0520 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
File dir = new File(".");
// 파일이나 디렉토리 정보를 File 객체로 받기
// => File은 디렉토리와 파일을 통칭하는 용어다.
//
File[] files = dir.listFiles();
for (File file : files) {
System.out.printf("%s %s %12d %s\n",
file.isDirectory() ? "d" : "-",
new Date(file.lastModified()),
file.length(),
file.getName());
}
}
}
ㄴ 파일이나 디렉터리 정보를 File 객체로 받기
=> 파일은 디렉터리와 파일을 통칭하는 용어
디렉토리에 들어있는 파일(디렉토리) 목록을 꺼낼 때 필터 적용하기
Exam0610.java
package com.eomcs.io.ex01;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FilenameFilter;
public class Exam0610 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
class JavaFilter implements FilenameFilter {
@Override
public boolean accept(File dir/* 부모 경로 */, String name /* 파일,디렉토리 이름 */) {
// 이 메서드는 list()에서 호출한다.
// 해당 폴더에 들어 있는 파일이나 디렉토리를 찾을 때 마다 호출한다.
// (하위 폴더 아래는 뒤지지 않는다)
// 이 메서드에서 해야 할 일은 찾은 파일이나 디렉토리를
// 리턴할 배열에 포함시킬지 여부이다.
// true를 리턴하면 배열에 포함되고,
// false를 리턴하면 배열에 포함되지 않는다.
// 파일,디렉토리 이름이 .java 로 끝나는 경우만 리턴 배열에 포함시키다.
// if (name.endsWith(".java"))
// return true; // 조회 결과에 포함시켜라!
// return false; // 조회 결과에서 제외하라!
return name.endsWith(".java");
}
}
File dir = new File(".");
// => 확장자가 .java 인 파일의 이름만 추출하기
// 1) 필터 준비
JavaFilter javaFilter = new JavaFilter();
// 2) 필터를 사용하여 디렉토리의 목록을 가져오기
String[] names = dir.list(javaFilter);
for (String name : names) {
System.out.println(name);
}
}
}
ㄴ 문제점
=> temp.java 는 디렉토리임

=> 현재의 필터는 파일 이름으로만 검사함
=> 파일인지 디렉토리인지 여부는 검사하지 않음
해결책
=>
Exam0611.java
package com.eomcs.io.ex01;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FilenameFilter;
public class Exam0611 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
class JavaFilter implements FilenameFilter {
@Override
public boolean accept(File dir, String name) {
// 해당 이름이 디렉토리 이름인지 파일 이름인지 알아내려면
// File 객체를 생성해야 한다.
//
File file = new File(dir, name);
// 디렉토리 정보와 이름을 합쳐 파일 객체를 생성할 수 있다.
// if (file.isFile() && name.endsWith(".java"))
// return true; // 조회 결과에 포함시켜라!
// return false; // 조회 결과에서 제외하라!
return file.isFile() && name.endsWith(".java");
}
}
File dir = new File(".");
// => 확장자가 .java 인 파일의 이름만 추출하기
// 1) 필터 준비
JavaFilter javaFilter = new JavaFilter();
// 2) 필터를 사용하여 디렉토리의 목록을 가져오기
String[] names = dir.list(javaFilter);
for (String name : names) {
System.out.println(name);
}
}
}
ㄴ 파일 이름만 추출
Exam0620.java
package com.eomcs.io.ex01;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileFilter;
public class Exam0620 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
class JavaFilter implements FileFilter {
@Override
public boolean accept(File file) {
// 이 메서드는 listFiles() 메서드에서 호출한다.
// 지정한 폴더에 들어 있는 파일이나 디렉토리를 찾을 때 마다 호출한다.
// 리턴 값 File[] 에 찾은 파일 정보를 포함시킬지 여부를 결정한다.
// true 이면 배열에 포함시키고,
// false 이면 배열에서 제외한다.
//
// if (file.isFile() && file.getName().endsWith(".java"))
// return true; // 조회 결과에 포함시켜라!
// return false; // 조회 결과에서 제외하라!
return file.isFile() && file.getName().endsWith(".java");
}
}
File dir = new File(".");
// => 확장자가 .java 인 파일의 이름만 추출하기
// 1) 필터 준비
JavaFilter javaFilter = new JavaFilter();
// 2) 필터를 사용하여 디렉토리의 목록을 가져오기
File[] files = dir.listFiles(javaFilter);
for (File file : files) {
System.out.printf("%s %12d %s\n", file.isDirectory() ? "d" : "-", file.length(),
file.getName());
}
}
}
=>
익명 클래스로 FileFilter 만들기
Exam0630.java
package com.eomcs.io.ex01;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileFilter;
public class Exam0630 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
FileFilter filter = new FileFilter() {
@Override
public boolean accept(File file) {
if (file.isFile() && file.getName().endsWith(".java"))
return true;
return false;
}
};
File dir = new File(".");
File[] files = dir.listFiles(filter);
for (File file : files) {
System.out.printf("%s %12d %s\n", file.isDirectory() ? "d" : "-", file.length(),
file.getName());
}
}
}

ㄴ 필터 객체를 한 개만 만들 것이라면 익명 클래스로 정의하는 것이 나음
=>
package com.eomcs.io.ex01;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileFilter;
public class Exam0640 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
File dir = new File(".");
File[] files = dir.listFiles(new FileFilter() {
@Override
public boolean accept(File file) {
if (file.isFile() && file.getName().endsWith(".java"))
return true;
return false;
}
});
for (File file : files) {
System.out.printf("%s %12d %s\n", file.isDirectory() ? "d" : "-", file.length(),
file.getName());
}
}
}

ㄴ 익명 클래스를 정의할 때
=> 객체를 사용할 위치에 익명 클래스를 정의하는 것이 코드를 더 읽기 쉽게 만듦
=>
람다로 FileFilter 만들기
Exam0650.java
package com.eomcs.io.ex01;
import java.io.File;
public class Exam0650 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
File dir = new File(".");
// 메서드 한 개짜리 인터페이스인 경우
// 람다(lambda) 문법을 사용하면 훨씬 더 간결하게 코드를 작성할 수 있다.
//
// lambda class
// => 메서드가 한 개짜리인 경우 lambda 표현식을 사용할 수 있다.
// => 문법:
// (파라미터, 파라미터, ...) -> 문장 한개
// (파라미터, 파라미터, ...) -> { 문장1; 문장2; 문장3;}
// () -> 문장 한개
// () -> {문장1; 문장2; 문장3;}
//
File[] files = dir.listFiles(file -> {
return file.isFile() && file.getName().endsWith(".java");
});
for (File file : files) {
System.out.printf("%s %12d %s\n", file.isDirectory() ? "d" : "-", file.length(),
file.getName());
}
}
}
=>
Exam0651.java
package com.eomcs.io.ex01;
import java.io.File;
public class Exam0651 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
File dir = new File(".");
// 메서드 한 개짜리 인터페이스인 경우
// 람다(lambda) 문법을 사용하면 훨씬 더 간결하게 코드를 작성할 수 있다.
// => expression 은 return 문장을 생략할 수 있다.
File[] files = dir.listFiles(file -> file.isFile() && file.getName().endsWith(".java"));
for (File file : files) {
System.out.printf("%s %12d %s\n", file.isDirectory() ? "d" : "-", file.length(),
file.getName());
}
}
}
활용: 필터와 Lambda 표현식을 사용하여 디렉토리 이름만 추출하라.
Exam0660.java
package com.eomcs.io.ex01;
import java.io.File;
public class Exam0660 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
File file = new File(".");
File[] files = file.listFiles(f -> f.isDirectory());
for (File f : files) {
System.out.printf("%s %12d %s\n",
f.isDirectory() ? "d" : "-",
f.length(),
f.getName());
}
}
}
활용 - 지정한 폴더 및 그 하위 폴더까지 모두 검색하여 파일 및 디렉토리 이름을 출력
Exam0710.java
package com.eomcs.io.ex01;
import java.io.File;
public class Exam0710 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
File dir = new File(".");
System.out.println(dir.getCanonicalPath());
printList(dir, 1);
}
static void printList(File dir, int level) {
// 현재 디렉토리의 하위 파일 및 디렉토리 목록을 알아낸다.
File[] files = dir.listFiles();
String indent = getIndent(level);
// 리턴 받은 파일 배열에서 이름을 꺼내 출력한다.
for (File file : files) {
System.out.print(indent);
if (file.isDirectory() && !file.isHidden()) {
System.out.printf("%s/\n", file.getName());
printList(file, level + 1);
} else if (file.isFile()) {
System.out.print("\\-- ");
System.out.printf("%s\n", file.getName());
}
}
}
static String getIndent(int level) {
StringBuilder strBuilder = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < level; i++) {
strBuilder.append(" ");
}
return strBuilder.toString();
}
}
ㄴ 레벨별로 출력하기
재귀함수


=>

ㄴ 팩토리얼
활용 - 지정한 폴더를 삭제하라.
Exam0720.java
package com.eomcs.io.ex01;
import java.io.File;
public class Exam0720 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// temp 디렉토리를 삭제하기
File dir = new File("temp");
deleteFile(dir);
}
static void deleteFile(File dir) {
// 주어진 파일이 디렉토리라면 하위 파일이나 디렉토리를 찾아 지운다.
if (dir.isDirectory()) {
File[] files = dir.listFiles();
for (File file : files) {
deleteFile(file);
}
}
dir.delete(); // 현재 파일이나 폴더 지우기
}
}
활용 - 지정한 폴더에서 .class 파일만 찾아 출력하기
Exam0730
package com.eomcs.io.ex01;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileFilter;
public class Exam0730 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
File dir = new File("bin/main");
System.out.println(dir.getCanonicalPath());
printClasses(dir);
}
static void printClasses(File dir) {
File[] files = dir.listFiles(new FileFilter() {
@Override
public boolean accept(File pathname) {
return pathname.isDirectory() || (pathname.isFile() && pathname.getName().endsWith(".class"));
}
});
for (File file : files) {
if (file.isDirectory()) {
printClasses(file);
} else {
System.out.printf("%s\n", file.getName());
}
}
}
}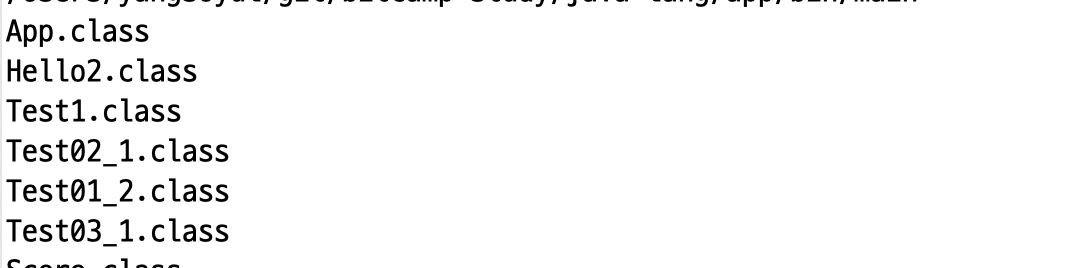
활용 - 클래스 파일 이름을 출력할 때 패키지 이름을 포함하라.
Exam0731.java
package com.eomcs.io.ex01;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileFilter;
public class Exam0731 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 클래스 이름을 출력할 때 패키지 이름을 포함해야 한다.
// 예) ch01.Test01
// 예) ch22.a.Test14
//
File dir = new File("bin/main");
System.out.println(dir.getCanonicalPath());
printClasses(dir, "");
}
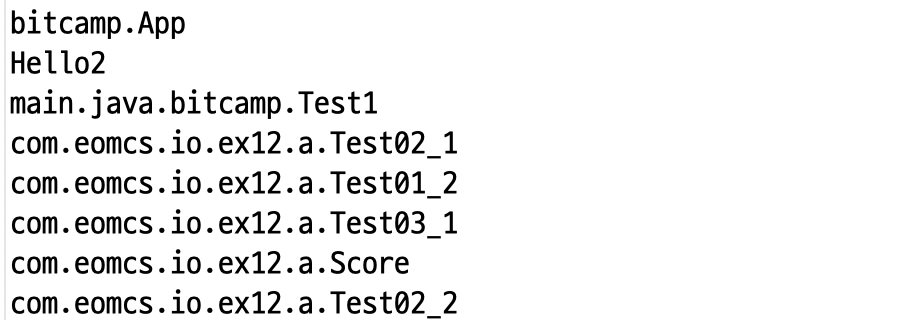
static void printClasses(File dir, String packageName) {
File[] files = dir.listFiles(new FileFilter() {
@Override
public boolean accept(File pathname) {
return pathname.isDirectory() || (pathname.isFile() && pathname.getName().endsWith(".class"));
}
});
if (packageName.length() > 0) {
packageName += ".";
}
for (File file : files) {
if (file.isDirectory()) {
printClasses(file, packageName + file.getName());
} else {
// path가 파일이면 패키지 이름과 파일 이름을 합쳐 출력하고 리턴한다.
// => 단 파일 이름에서 .class 확장자 명은 제외한다.
// => 파일 명이 Hello.class 이고 패키지명이 aaa.bbb 라면
// 출력할 이름은 aaa.bbb.Hello 이다.
System.out.println(packageName + file.getName().replace(".class", ""));
}
}
}
}
=>
람다 문법 활용
Exam0731.java
package com.eomcs.io.ex01;
import java.io.File;
public class Exam0732 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 클래스 이름을 출력할 때 패키지 이름을 포함해야 한다.
// 예) ch01.Test01
// 예) ch22.a.Test14
//
File dir = new File("bin/main");
System.out.println(dir.getCanonicalPath());
printClasses(dir, "");
}
static void printClasses(File dir, String packageName) {
// 기존의 익명 클래스를 람다 문법으로 교체한다.
File[] files = dir.listFiles(
f -> f.isDirectory() || (f.isFile() && f.getName().endsWith(".class")));
if (packageName.length() > 0) {
packageName += ".";
}
for (File file : files) {
if (file.isDirectory()) {
printClasses(file, packageName + file.getName());
} else {
System.out.println(packageName + file.getName().replace(".class", ""));
}
}
}
}


